One Outpatient Procedure. Lasting Lung Health.
The dNerva® Lung Denervation System is a novel, catheter-based system used to treat overactive airway nerves in a procedure called Targeted Lung Denervation. This first-of-its kind technology addresses underlying COPD pathophysiology to help preserve lung health.1,2
Lung Denervation
Changing Lung Physiology to Improve Lung Health
Lung dNervation is performed in both lungs during a single 90-minute outpatient procedure under general anesthesia. Most patients return home the same day as treatment.
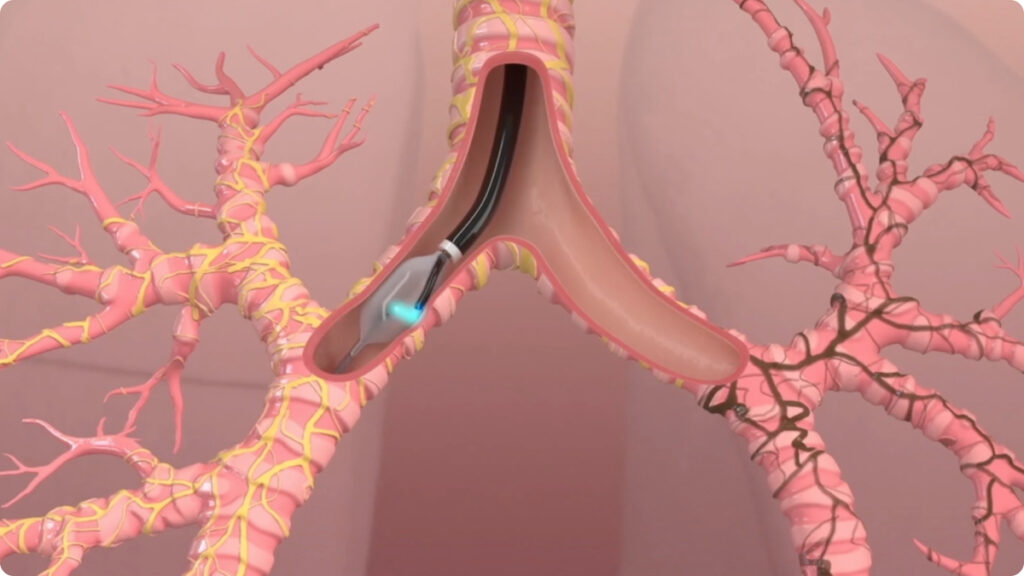
The dNerva RF catheter is passed through a standard flexible bronchoscope into the mainstem bronchi of each lung. Energy is delivered for 2 minutes to complete an ablation in each quadrant of the airway. The catheter will be rotated 3 times to complete a full circumferential ablation. The bronchoscope will then be placed into the other lung and the process repeated. Both lungs are treated in a single procedure.
The ablation permanently disrupts pulmonary nerve input to the lung to achieve durable lung denervation.
Non-Surgical, Outpatient Treatment
The Procedure
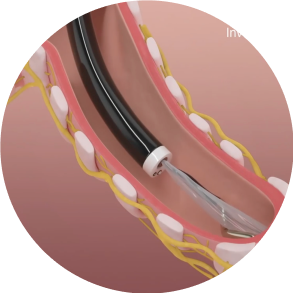
Position
The dNerva Catheter threads through the working channel of the bronchoscope and is positioned in the main bronchi.
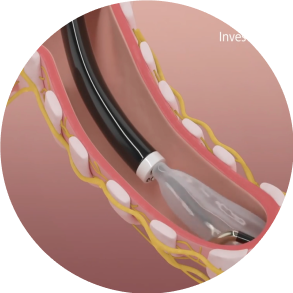
Inflate
The conduit and balloon are inflated by circulating the coolant through the catheter which brings the electrode in contact with the airway wall.
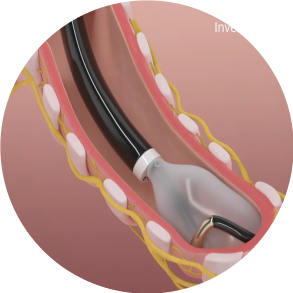
Confirm
Confirm good contact of the electrode with the airway wall and that adequate distance from the esophagus is achieved.
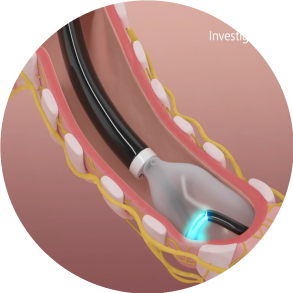
Activate
Energy activation lasts approximately two minutes per quadrant. The catheter will be rotated 3 times to achieve a full circumferential ablation in each airway.
Post-Procedure
The procedure will last about 70-100 minutes and patients can expect to go home the same day. Post-procedure follow-up care is consistent with advanced bronchoscopic procedures.
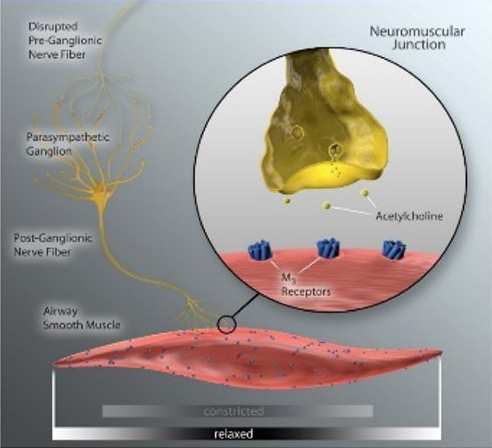
How it Works
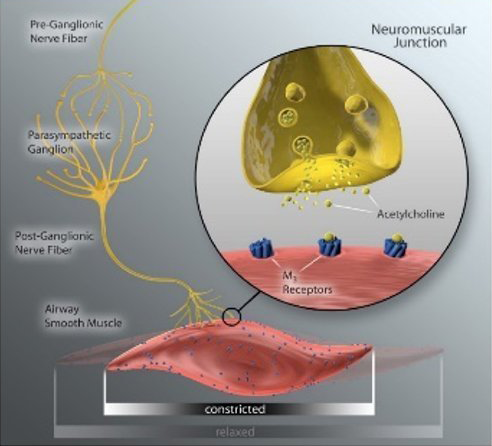
The human lung is extensively innervated by pulmonary branches of the vagus nerve which impact lung physiology in health and disease (6, 8 ). In COPD, acetylcholine released from parasympathetic airway nerves controls smooth muscle tone, reflex bronchoconstriction, mucus hypersecretion, and airway inflammation, which contribute to disease progression and presents as dyspnea in patients with obstructive lung disease (9).
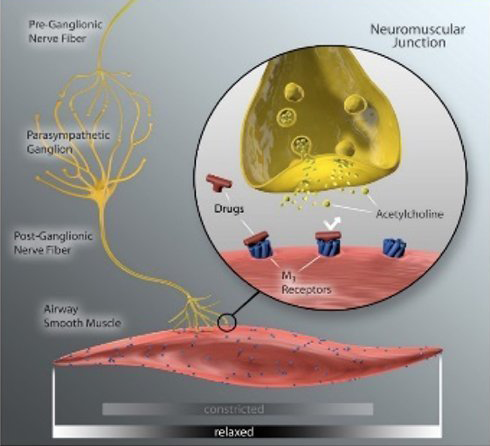
Anticholinergic inhaler therapy targets the parasympathetic nerve system in COPD, by preventing binding of acetylcholine to M3 receptors on airway smooth muscle. Lung denervation permanently disrupts neuronal acetylcholine release, providing a therapeutic complement to muscarinic receptor blockade in the lung. (10)
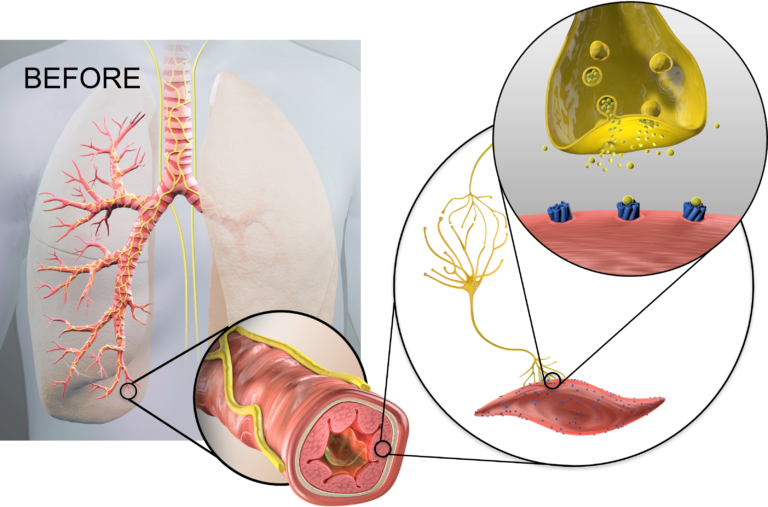
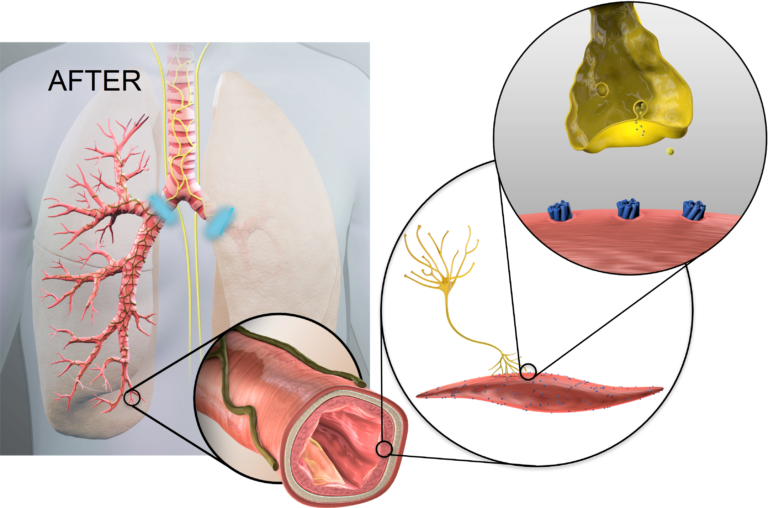
Before & After Slider
The dNerva Difference
After lung denervation, less acetylcholine is produced, helping to relax overactive airways, reduce bronchoconstriction, and decrease mucus hypersecretion.
Lung denervation creates an “always on” bronchodilator effect, to help improve clinical stability in patients with COPD.
Discover our Products
Dual Cooled™ Lung Denervation
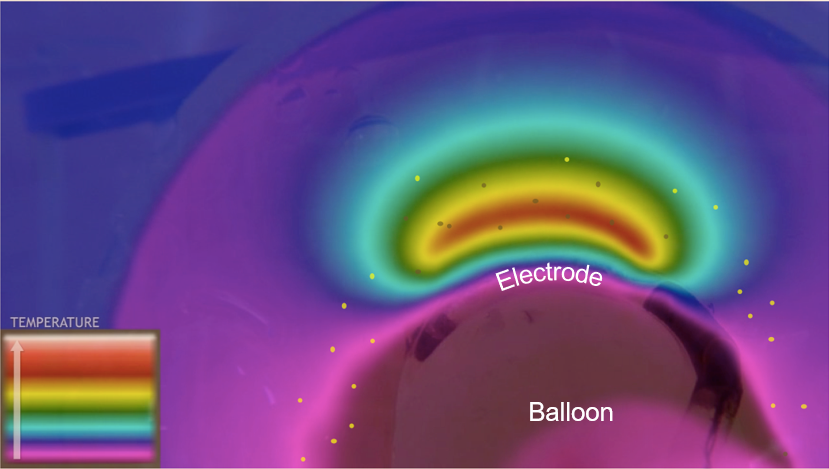
The dNerva lung denervation system actively manages delivery of RF energy while simultaneously cooling within the treated airway. During energy delivery, active cooling of the esophagus provides additional protection.
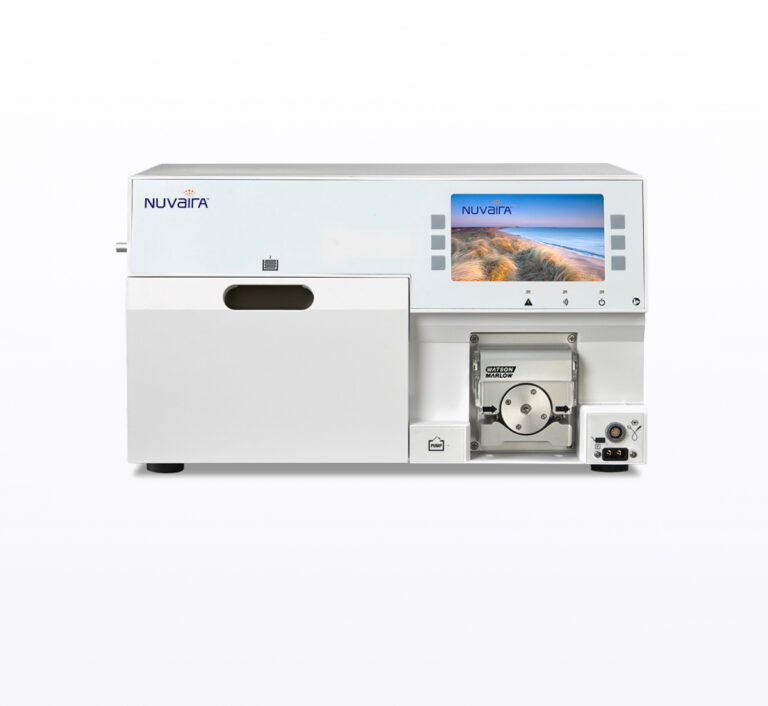

Nuvaira Console
The Nuvaira Console includes a thermoelectric plate and pump that cools the fluid circulating through the dNerva catheter to protect the airway wall during Radio-frequency energy delivery. The Nuvaira Console also includes graphical user interface with a prompt screen to control the console and guide the user.
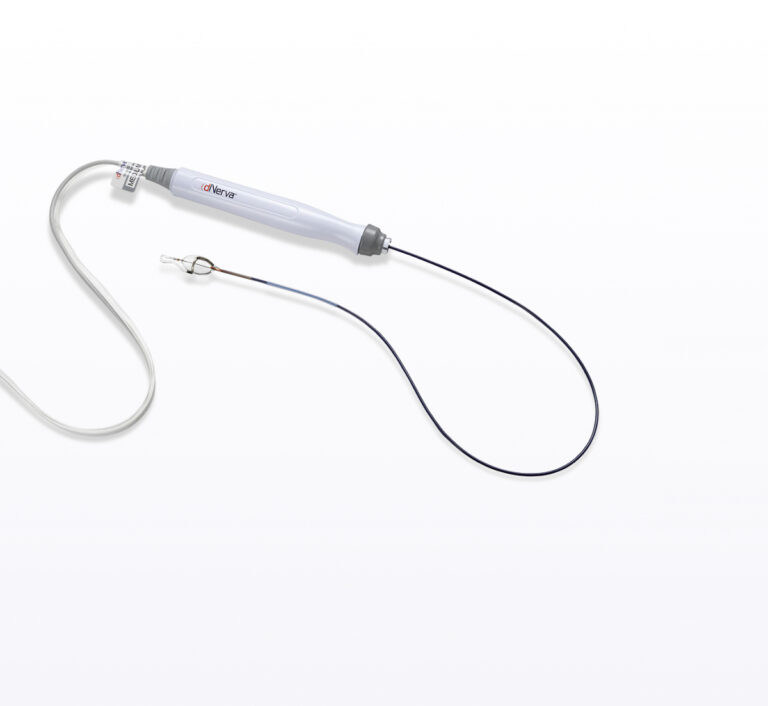
dNerva Catheter
The dNerva Catheter is a specialized, patented disposable component that is compatible with most flexible bronchoscopes utilizing working channels down to 2.8mm in diameter. The distal balloon and electrode assembly have been designed to collapse to fit through the bronchoscope’s working channel. The catheter is available in multiple sizes.
Esophageal Cooling Catheter
The EsoCool ™ esophageal cooling catheter is designed to cool the esophagus during RF ablation in the lung.
dNerva Lung Denervation System
Safety Features
Cooling to Protect Airway Walls
During RF energy activation, coolant is circulated through the electrode and through the catheter balloon, providing cooling to all touchpoints within the airway wall. dNerva catheters provide cooling protection to the inner surface of the airway wall while focusing heating effects to the depth of the pulmonary nerves on the outside of the airway.
As an additional safety enhancement to the dNerva procedure, an esophageal cooling catheter is used.